OpenGradient Architecture
OpenGradient runs on the Hybrid AI Compute Architecture (HACA) — a network design built around the observation that AI workloads cannot be handled the same way as financial transactions.
In a conventional blockchain, every validator re-executes every transaction. This works for token transfers and state updates, but not for AI inference. Running a model takes orders of magnitude more time, requires specialized hardware (GPUs), and produces outputs that are non-deterministic by nature. Asking every validator to independently re-run a model inference is impractical — it does not scale, it wastes compute, and it introduces latency that makes real applications impossible.
HACA addresses this by splitting the network into specialized node types, each optimized for a specific role. Inference nodes run models. Full nodes verify proofs and maintain the ledger. Data nodes provide trusted access to external information. Storage is handled off-chain on Walrus. No single node type does everything — instead, they coordinate to deliver a system that is both fast and verifiable.
The underlying blockchain uses CometBFT consensus and is currently in testnet.
Why Node Specialization
The decision to specialize nodes is not arbitrary. It follows directly from the constraints of AI workloads:
AI inference is expensive and heterogeneous. A small classification model and a 70B-parameter LLM have wildly different hardware requirements. A single validator set with uniform capabilities would either be over-provisioned for simple models or incapable of running large ones. Dedicated inference nodes can be provisioned with the right hardware for their workload.
Verification does not require re-execution. You do not need to re-run a model to verify it ran correctly. TEE attestations prove the enclave was not tampered with. ZKML proofs provide mathematical certainty that a specific model produced a specific output. This means verification nodes (full nodes) can be lightweight — they check proofs, not run models.
Data access needs isolation. External data — price feeds, API responses, social media posts — must be fetched from third-party sources. Doing this inside a TEE enclave ensures the data was not intercepted or modified by the node operator. Separating data access into dedicated nodes keeps the trust boundary clean.
Storage scales differently than compute. Model files can be gigabytes. Proof data can be large. Storing all of this on-chain would make the ledger unusable. Off-chain storage with on-chain references (blob IDs) keeps the ledger lean while maintaining data availability through Walrus.
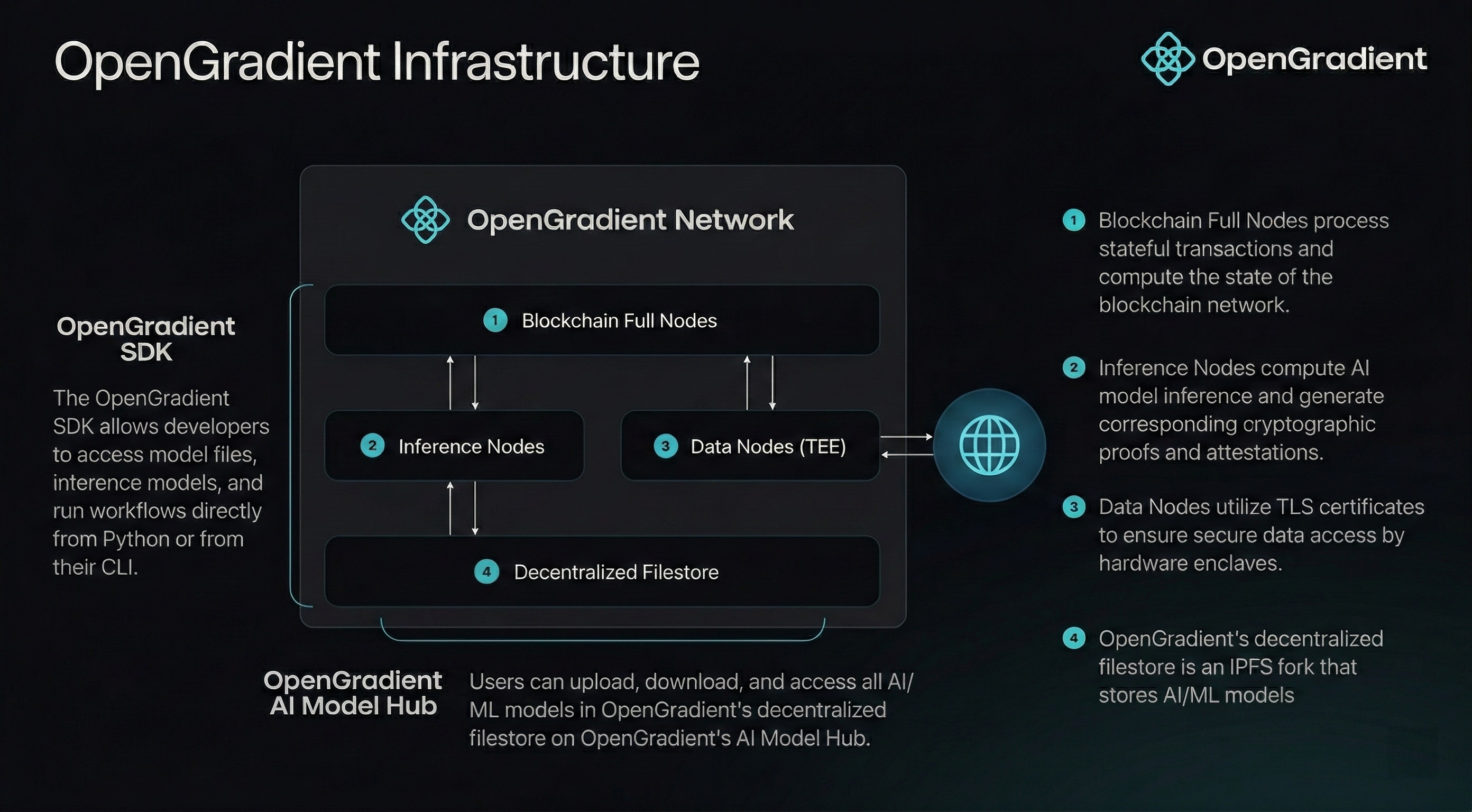
Node Types
How Nodes Coordinate
The key to HACA is that nodes interact through well-defined interfaces rather than sharing responsibilities:
Registration
Before any inference node can serve requests, it must register with the network through full nodes. For TEE-enabled nodes, registration includes hardware attestation verification — proving the enclave runs approved, untampered code. This registration is recorded on-chain via smart contracts, so it is auditable by anyone and not controlled by any single party.
Registration also publishes the node's TLS certificate and signing key, both generated inside the enclave. This means clients can establish encrypted connections directly with attested nodes, with trust rooted in on-chain verification rather than certificate authorities.
See Consensus — Inference Node Registry for the full registration flow.
Inference (The Fast Path)
When a user requests inference:
- The request is routed directly to an appropriate inference node — the blockchain is not in the critical path.
- The inference node executes the model (locally or via a TEE-proxied provider call).
- The result is returned to the user immediately.
There is no block confirmation, no validator voting, and no consensus delay in this path. The user gets a response with the same latency they would expect from a centralized API.
Settlement (The Verification Path)
After inference completes, the proof is settled asynchronously:
- The inference node generates a proof — a TEE attestation, a ZKML proof, or a signed result depending on the verification method.
- The proof is submitted to full nodes.
- Full nodes verify the proof during the next consensus round.
- Once 2/3+ validators agree, the proof is permanently recorded on the ledger.
For large proofs (like ZKML), only a reference (blob ID) is stored on-chain, with the full proof data on Walrus.
Payment
Payment settlement depends on the inference type:
- LLM inference (x402): Payment uses
$OPGtokens on Base Sepolia, settled through the Permit2 protocol. The facilitator verifies payment before inference is authorized. - ML inference (PIPE): Payment is handled natively on the OpenGradient chain as part of the transaction.
In both cases, payment verification and inference execution are separate concerns, handled by different components.
Verification Spectrum
Not all inference needs the same level of trust. HACA supports a spectrum of verification methods, and developers choose what fits their use case:
| Method | Mechanism | Overhead | When to Use |
|---|---|---|---|
| TEE | Hardware attestation proves inference ran in a secure enclave with approved code | Negligible | LLM inference, privacy-sensitive workloads, most production use cases |
| ZKML | Zero-knowledge proof mathematically proves a specific model produced a specific output | 1000-10000x | High-stakes ML models where cryptographic certainty is required |
| Vanilla | Signature verification only — no proof of correct execution | None | Low-risk workloads, prototyping, non-critical inference |
This is an intentional design choice. Forcing ZKML on every inference would make the network unusable for LLMs. Allowing only TEE would exclude use cases that need mathematical proof. The verification spectrum lets the network serve everything from chatbots to on-chain DeFi models.
You can even mix verification methods within a single transaction — TEE for one model, ZKML for another — depending on what each inference is used for.
Design Principles
For a deeper exploration of the architectural thinking behind HACA — including why conventional approaches fail for AI, how the separation of execution and verification creates new possibilities, and what trade-offs were made — see Design Principles.
Diagram
Below is a diagram of the HACA components and their interactions:
Next Steps
- Full Nodes — How validators verify proofs and maintain the ledger
- Inference Nodes — How models are executed and proofs generated
- Data Nodes — How external data is fetched with TEE guarantees
- Storage — How Walrus provides decentralized model and proof storage
- Design Principles — The reasoning behind HACA's architecture
- Consensus — CometBFT consensus and the settlement layer
